| There’s no such thing as short-term type 2 diabetes treatment. Managing this disease requires careful and continual attention to your health. The good news: Some very basic lifestyle adjustments — eating healthy and getting regular exercise — will go a long way toward helping you manage type 2 diabetes. |
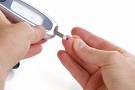
| Diabetes Treatment: The Basics Type 2 diabetes treatment revolves around managing blood glucose levels, also called blood sugar levels. Folks with type 2 diabetes face two problems: Their cells don’t take in glucose as well as they used to because they’ve become resistant to insulin, a hormone that aids in processing glucose. And their bodies are not producing as much insulin as they used to because the organ that creates the hormone, the pancreas, has been damaged by strain and overwork. If you don’t manage your blood sugar levels, diabetes can cause terrible systemic damage to your body. You could suffer kidney damage, heart disease, or blindness. In extreme cases, diabetes can necessitate amputation of limbs. Proper diabetes treatment requires a few basic skills. These include: Performing regular tests on your blood glucose levels.Eating right and exercising.Taking the necessary medications, including insulin. Diabetes Treatment: Blood Glucose Testing Since managing blood sugar levels is key to diabetes treatment, it’s important to perform regular tests. You can do these tests yourself, with items found at any pharmacy and most grocery stores: A glucose meter, Alcohol pads, Sterile lancets, & Test strips. To perform a blood glucose test: After washing and drying your hands, use an alcohol pad to swab the area you’re going to prick. Most people prick a fingertip, but some meters let you use blood from your forearm, thigh, or the fleshy part of your hand.Prick yourself using a sterile lancet, an instrument that looks like a pen with a pin tip at the end, and place a drop of blood on a test strip.Feed the strip into the glucose meter, which will tell you your blood sugar level. Check your blood sugar regularly. Your doctor will set an initial testing schedule with you. Diabetes Treatment: Diet and Exercise A good diet and consistent exercise help stabilize blood sugar levels and help you lose weight — a great benefit in managing diabetes, says R. Paul Robertson, MD, president, Medicine and Science, of the American Diabetes Association, and professor of medicine and pharmacology at the University of Washington, Seattle. “The more overweight you are, the more important it is to lose that weight,” Dr. Robertson says. “It will make the insulin your body makes more effective. You can take less insulin, if you are leaner, to get the same level of glucose control.” A good diet for diabetes treatment includes: Regularly timed meals and snacks. Consistent eating patterns can help you manage your blood glucose levels.High-fiber carbohydrates. These digest slowly and keep blood sugar levels stable. Whole grains, brown rice, and dried beans are some options.Vegetables and fruits. Fill your plate with non-starchy vegetables like broccoli, spinach, and carrots, and reduce portions of everything else.Foods low in saturated fat and free of trans-fats. Choose lean meats and fish. Read food labels for fat content.Drink water. Choose water or fresh fruit juices over sugary colas or fruit punches. You should exercise for at least 30 minutes a day, five days a week with moderate intensity (brisk walking, yard work, swimming, bicycling, etc.). If possible, get some exercise every day. Diabetes Treatment: Insulin and Medications If you cannot fully control diabetes with diet and exercise, you may need to take insulin or medications to manage blood-sugar levels. Insulin. Insulin comes in several forms, ranging from fast-acting to long-acting. Talk with your doctor about the type of insulin that will best treat your diabetes.Oral medications. There are five different types of medications: sulfonylureas, meglitinides, biguanides, thiazolidinediones, and alpha-glucosidase inhibitors. All work in different ways to reduce your blood glucose level. Timing is important when using insulin or medications. Talk with your doctor about what schedule you should follow. The right combination of diet, exercise, and monitoring will go far to keep your diabetes under control. |











